On the latest Journal of Applied Crystallography, the research team composed of Zhongzheng Zhou, Chun Li, and Longlong Fan (the research team of Dong Yuhui, a researcher from the Institute of High Energy Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences) published a research article entitled "Denoising an X-ray image by exploring the power of its physical symmetry", bringing revolutionary progress to X-ray imaging technology. This study combines the inherent physical symmetry of X-ray images with the MAE algorithm in the field of computer vision to propose the Symmetrical Masked AutoEncoder algorithm (see Figure 1), which enables neural networks to achieve efficient and accurate denoising only on low signal-to-noise ratio data after pre-training, without the need for high signal-to-noise ratio data fine-tuning. Compared with the MAE pre-training method, using a small batch of high signal-to-noise ratio data fine-tuning models results in better denoising and physical information recovery of X-ray images.
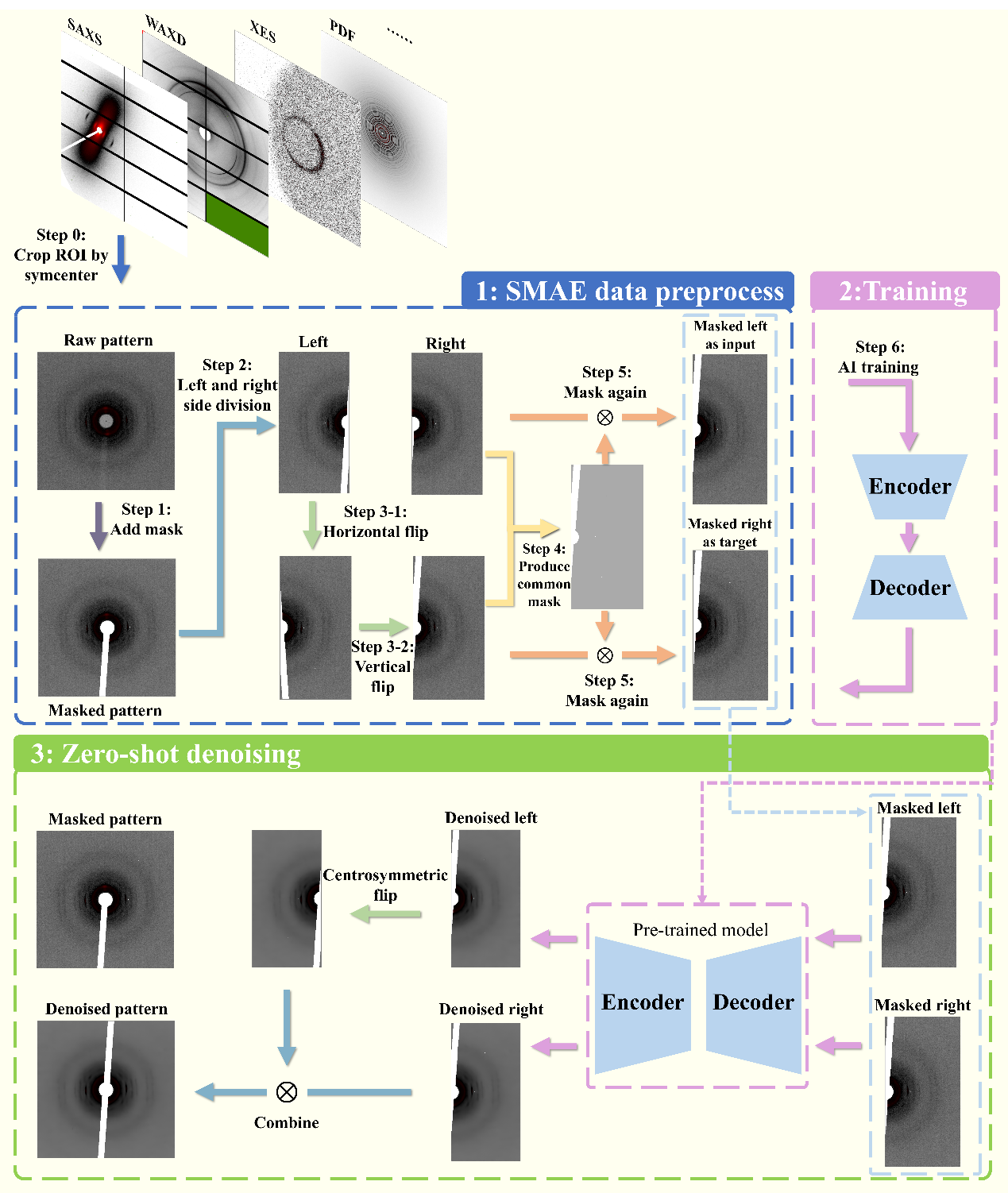
The research team applied the algorithm to real experimental data of SAXS/WAXD (see Figure 2) and atomic pair distribution function experiment PDF (see Figure 3), and fine tuned high signal-to-noise ratio data after pre-training with multiple algorithms (MAE method), Zero-shot Noise2Noise, Supervised learning method, multiple samples (bones, bamboo, metallic glass) and multiple physical information were used to evaluate the physical information recovery ability of SAXS/WAXD surface scan experimental data and time-resolved PDF data, and the best results were achieved. The research team stated: "Combining physical prior information with deep learning techniques to achieve denoising of massive low signal-to-noise ratio data will have a huge impact on experimental modes that require high throughput, cross scale, and in situ inspection."
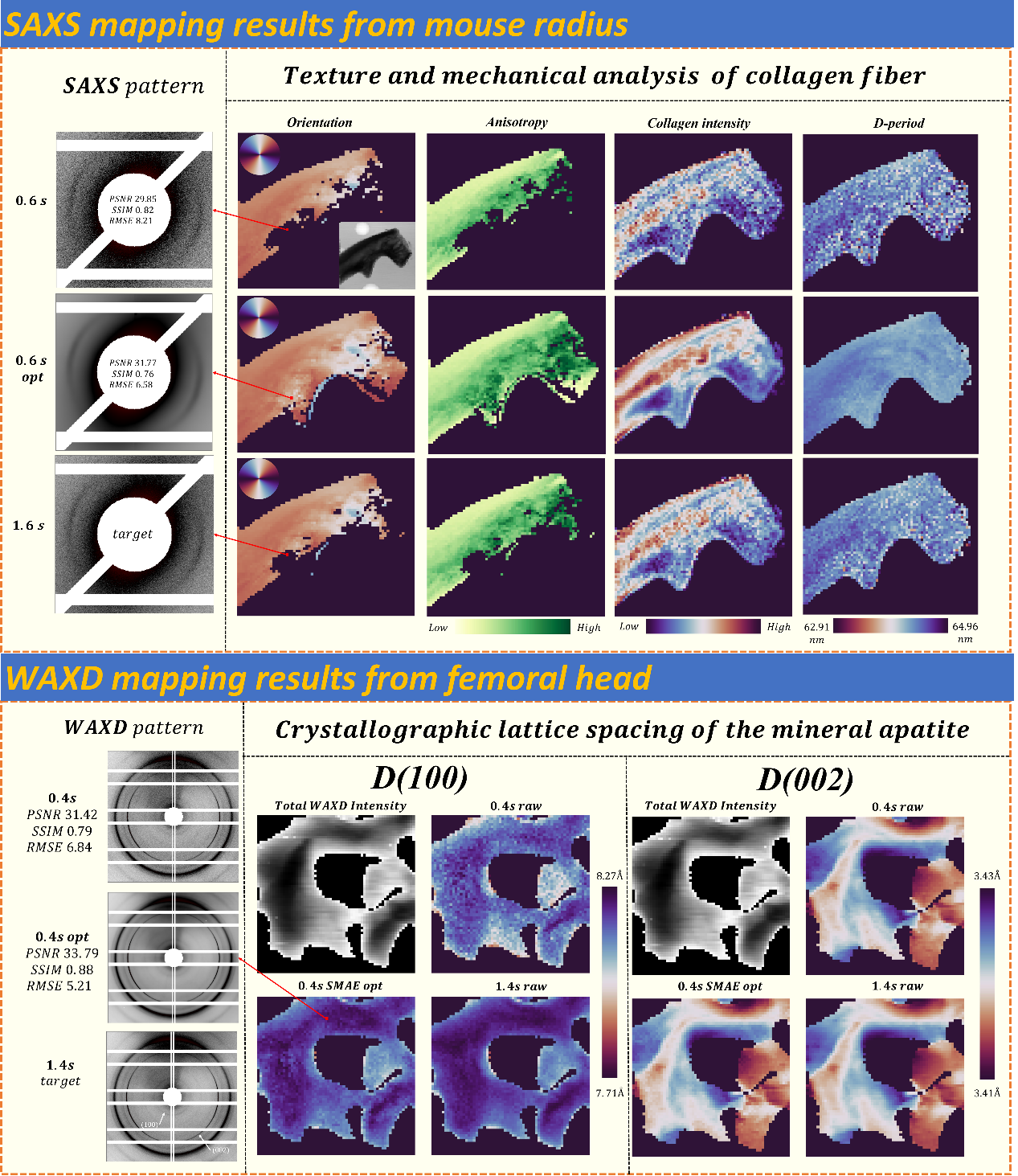
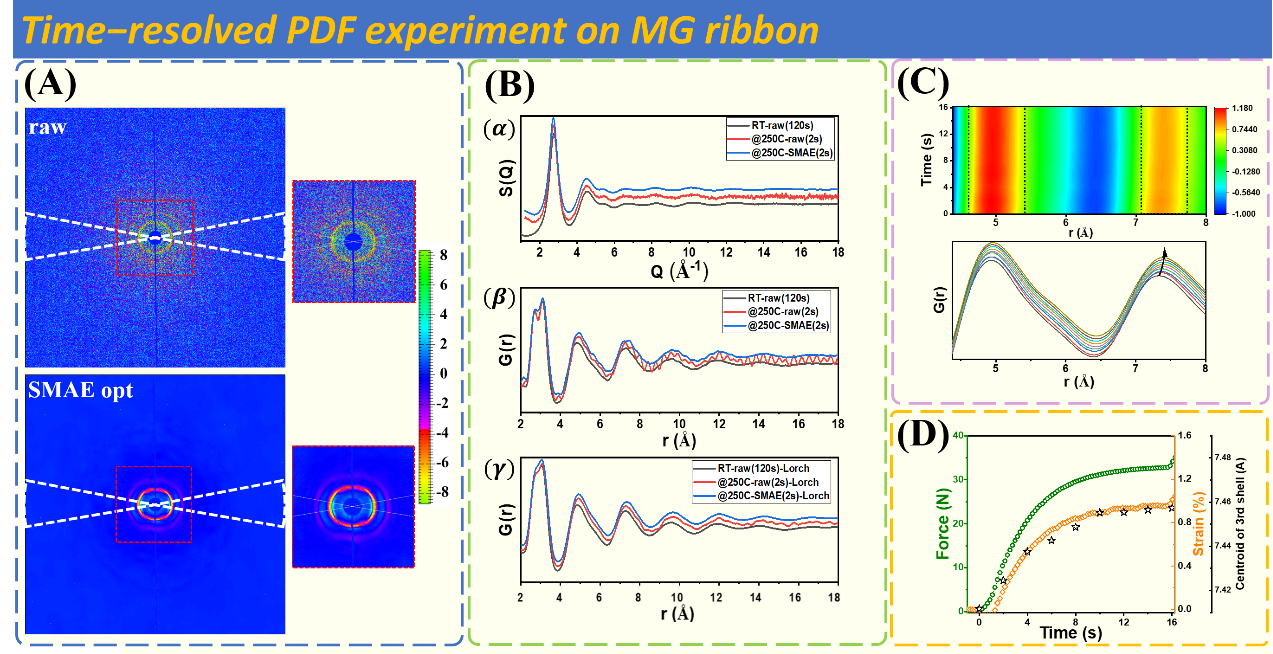
The research team cooperated with many institutions, including the Beijing Synchrotron Radiation Facility, the Institute of High Energy Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the University of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the China Spallation Neutron Source Science Center in Dongguan, Beijing Jishuitan Hospital, the Capital Medical University and the Computer Vision Laboratory of the Federal Institute of Technology in Zurich, Switzerland, to ensure the preciseness and universality of the research.
For more details, please visit the online link or DOI of the article, or view the complete article in the Journal of Applied Crystal+detailed index. For open source code, please visit: https://github.com/zzZhou8/SMAE.